Binding Free Energy Calculations of HIV Protein Enzymes
HIV AIDS is a deadly disease that currently affects the life of millions of people infected worldwide. Using high performance computing clusters (XSEDE resources) and distributed computing networks (Temple Grid and IBM World Community Grid), I was one of leading members on performing massive-scale binding free energy calculations (thousands of ligands and millions of replicas) use our BEDAM method to improve docking predictions for discovering potent inhibitors against three major protein enzymes which play important roles in the life cycle of HIV viruses: HIV-1 protease(PR), integrase (IN), and reverse transcriptase (RT). Please check the related project, FightAIDS@Home on World Community Grid.
- Junchao Xia, William Flynn, Emilio Gallicchio, Keith Uplinger, Jonathan D. Armstrong, Stefano Forli, Arthur J. Olson, and Ronald M. Levy, " Massive-Scale Binding Free Energy Simulations of HIV Integrase Complexes Using Asynchronous Replica Exchange Framework Implemented on the IBM WCG distributed network," J. Chem. Info. Model. 59, 1382 (2019).
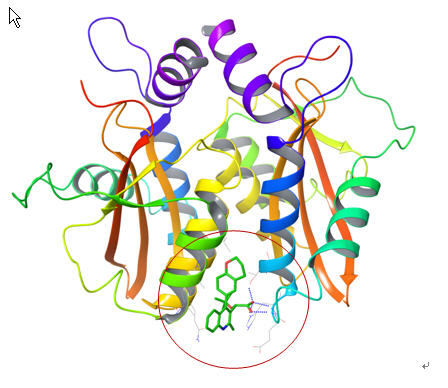
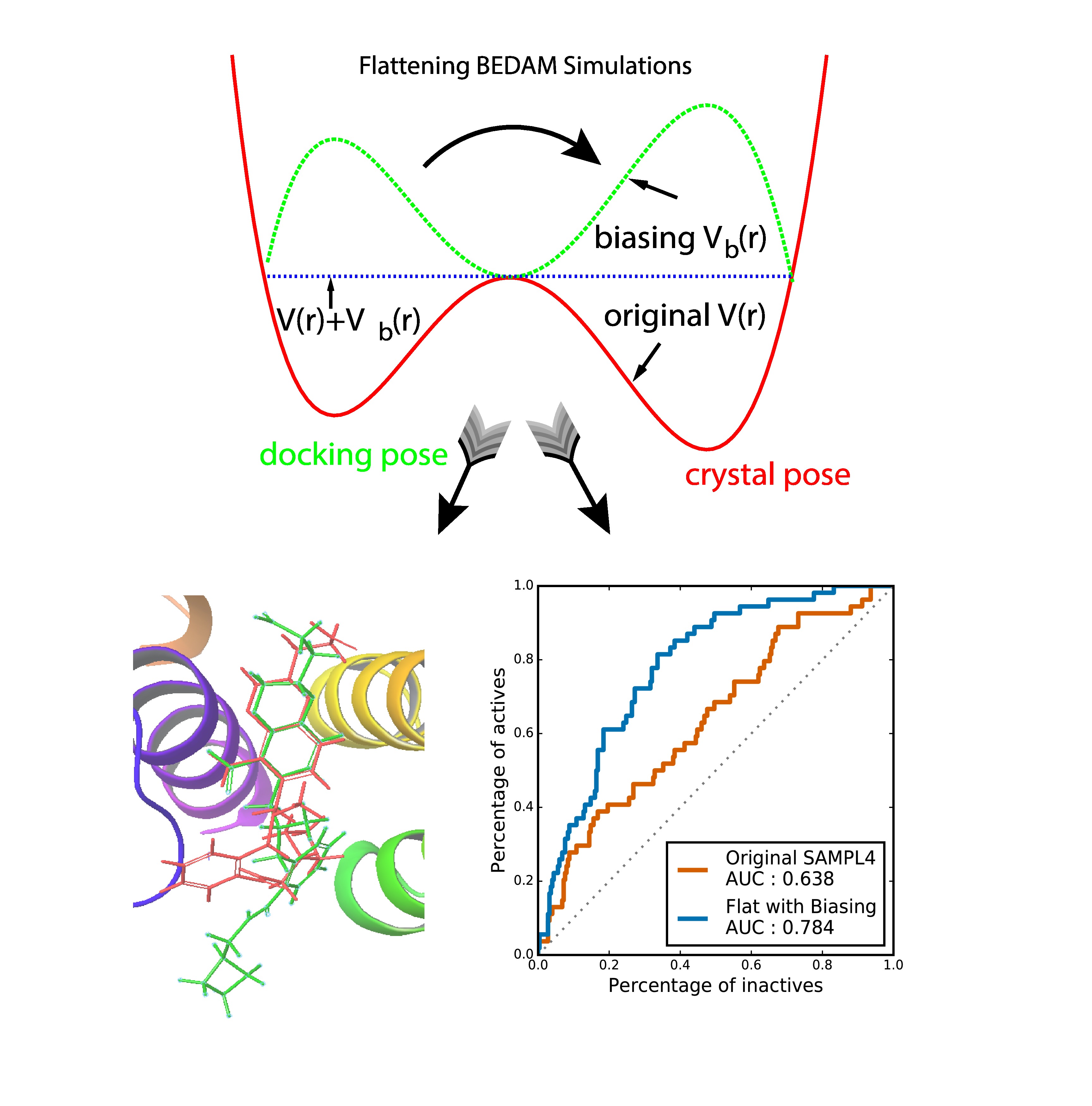
- Junchao Xia, William Flynn, and Ronald Levy, " Improving prediction accuracy of binding free energies and poses of HIV integrase complexes using the binding energy distribution analysis method with flattening potentials," J. Chem. Info. Model. 58, 1356 (2018).